622. Design Circular Queue
문제
Design your implementation of the circular queue. The circular queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle, and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called "Ring Buffer".
One of the benefits of the circular queue is that we can make use of the spaces in front of the queue. In a normal queue, once the queue becomes full, we cannot insert the next element even if there is a space in front of the queue. But using the circular queue, we can use the space to store new values.
Implement the MyCircularQueue class:
MyCircularQueue(k)Initializes the object with the size of the queue to be k.int Front()Gets the front item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.int Rear()Gets the last item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.boolean enQueue(int value)Inserts an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.boolean deQueue()Deletes an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.boolean isEmpty()Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. boolean isFull() Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. You must solve the problem without using the built-in queue data structure in your programming language.
예제 입출력
Input
["MyCircularQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "Rear", "isFull", "deQueue", "enQueue", "Rear"]
[[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
Output
[null, true, true, true, false, 3, true, true, true, 4]
Explanation
MyCircularQueue myCircularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(1); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(2); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(3); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return False
myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 3
myCircularQueue.isFull(); // return True
myCircularQueue.deQueue(); // return True
myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return True
myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 4
참고
You can read the full description here.
풀이 1
접근법
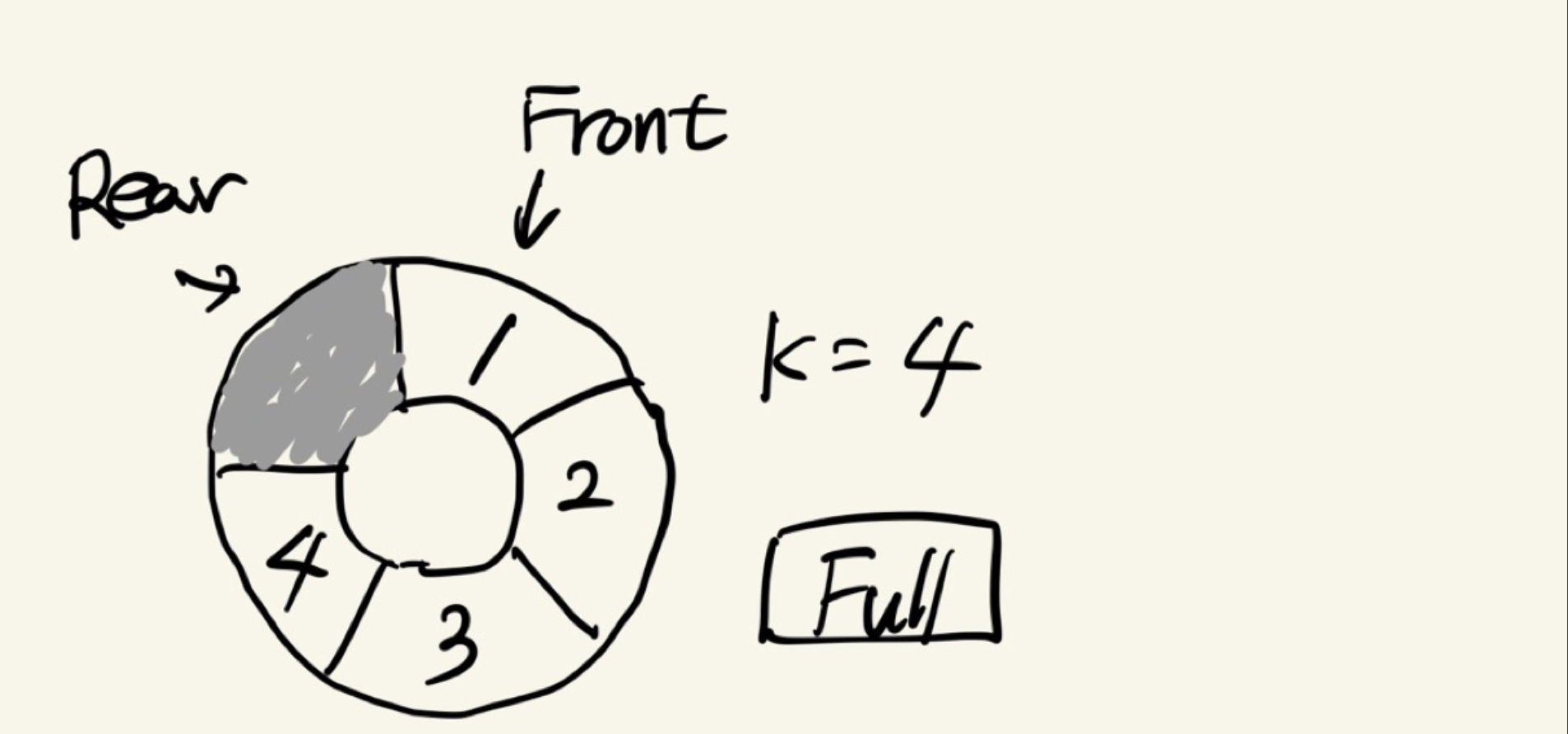
- 배열을 이용합니다. k+1 개의 공간을 이용합니다.
- 인덱스 front와 rear를 관리합니다. front는 첫 원소를, rear는 맨 마지막 원소 다음 공간을 가리키도록 합니다.
참고용 그림
구현 코드
class MyCircularQueue:
def __init__(self, k: int):
self.queue = [-1 for _ in range(k + 1)]
self.front = 0
self.rear = 0
self.size = k + 1
def enQueue(self, value: int) -> bool:
if self.isFull():
return False
else:
self.queue[self.rear] = value
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.size
return True
def deQueue(self) -> bool:
if self.isEmpty():
return False
else:
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.size
return True
def Front(self) -> int:
if self.isEmpty():
return -1
else:
return self.queue[self.front]
def Rear(self) -> int:
if self.isEmpty():
return -1
else:
return self.queue[((self.rear - 1) + self.size) % self.size]
def isEmpty(self) -> bool:
return self.front == self.rear
def isFull(self) -> bool:
return (self.rear + 1) % self.size == self.front
책에 있는 풀이
참고
원본 코드는 여기에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
풀이 2
접근법
- Front, Rear는 Full 과 Empty 상태가 동일해서 None 인지 여부를 한 번 더 확인해주어야 합니다.
참고용 그림
구현 코드
class MyCircularQueue:
def __init__(self, k: int):
self.q = [None] * k
self.maxlen = k
self.p1 = 0
self.p2 = 0
# enQueue(): 리어 포인터 이동
def enQueue(self, value: int) -> bool:
if self.q[self.p2] is None:
self.q[self.p2] = value
self.p2 = (self.p2 + 1) % self.maxlen
return True
else:
return False
# deQueue(): 프론트 포인터 이동
def deQueue(self) -> bool:
if self.q[self.p1] is None:
return False
else:
self.q[self.p1] = None
self.p1 = (self.p1 + 1) % self.maxlen
return True
def Front(self) -> int:
return -1 if self.q[self.p1] is None else self.q[self.p1]
def Rear(self) -> int:
return -1 if self.q[self.p2 - 1] is None else self.q[self.p2 - 1]
def isEmpty(self) -> bool:
return self.p1 == self.p2 and self.q[self.p1] is None
def isFull(self) -> bool:
return self.p1 == self.p2 and self.q[self.p1] is not None